Introduction. The main problem of osmotic power stations is high resistance of the membranes[1],[2]. Earlier we suggested the concept of concentration galvanic cell, working on salt and fresh water [3]. The concentration galvanic cell could use more thin membranes, than traditional osmotic power station. But non-membrane device could be more powerful, than any another device with semi-permeable membrane with the same size.
Non-membrane device.
We developed the concept of non-membrane way of electric power generation by mixing fresh and salt water.
The scheme of ion separation we can see in Fig. 1
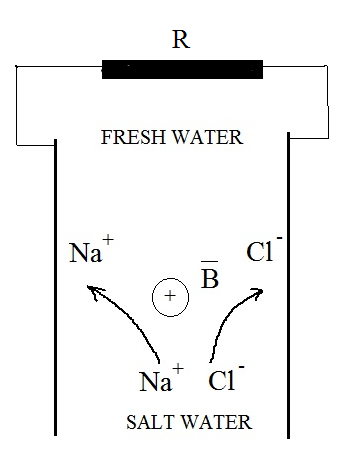
Fig 1. The scheme of ions separation in magnetic field
Na+ and Cl- ions drifts from salt to fresh water. Their trajectories are curved by the magnetic field. So Na+ ions are accumulates near one electrode and Cl- ions near another. It is the reason of potential difference appearance.
When potential difference (∆ φ) will equals 1,8 V it will be enough to carry out the reaction:
2H2O+2e=H2+OH-
2Cl- —2e=Cl2
To avoid Cl2 releasing to the atmosphere it is possible to cover electrodes by the gas adsorbent and sometimes change the direction of magnetic field or replace the electrodes.
Until ∆ φ<1,8V we will have no current, so, no electric power will generate
This potential difference could be calculated as
∆ φ=vBl, where
“B” is magnetic induction,
“l” is the distance between electrodes and v is the effective velocity of ions drift.
It is rather difficult to calculate in theory, but it is easy to carry out an experiment. The materials for experiment we can see in Fig.2
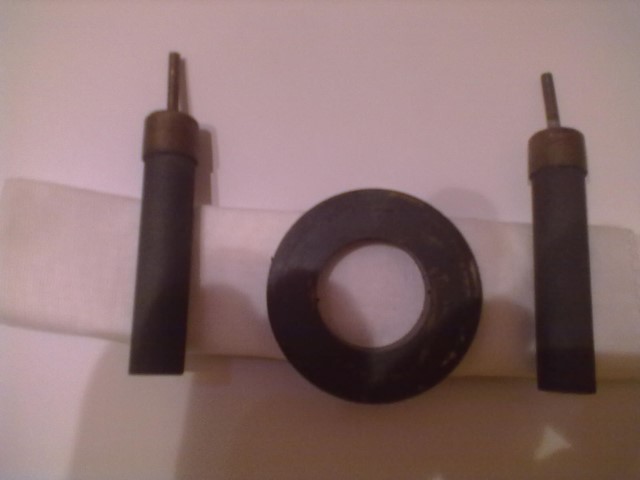

Fig. 2. Materials for experiment
We have two graphite electrodes, magnet from radio speaker and textile (in another experiment paper) in salt water from one side and fresh water from another.
The distance between electrodes was 0,03 m and ∆ φ was 0.06V (Fig 3). It is necessary to add, that this potential difference never appear immediately. It requires a time (about an hour) to get maximum potential difference.
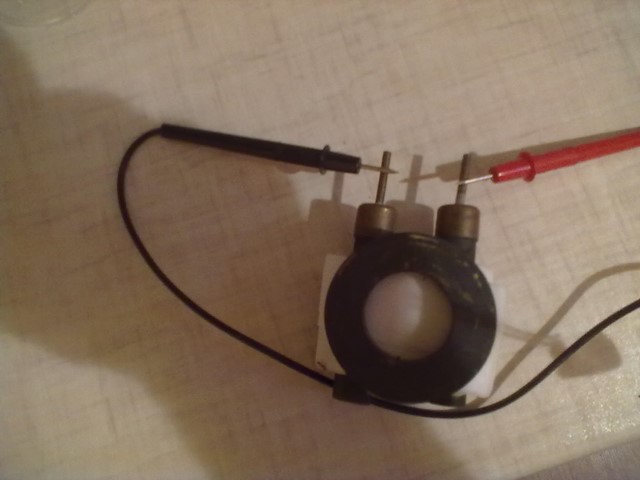

Fig. 3. Experiment
So, even in such weak magnetic field it is enough 0.9 m between electrodes to obtain ∆ φ in 1,8V, which is necessary for current appear.
Using more powerful magnet (Fig. 4) and distance 0.06 m between electrodes we obtain ∆ φ=0.22 V. In this case to begin power generating distance between electrodes could be only 0.35 m.
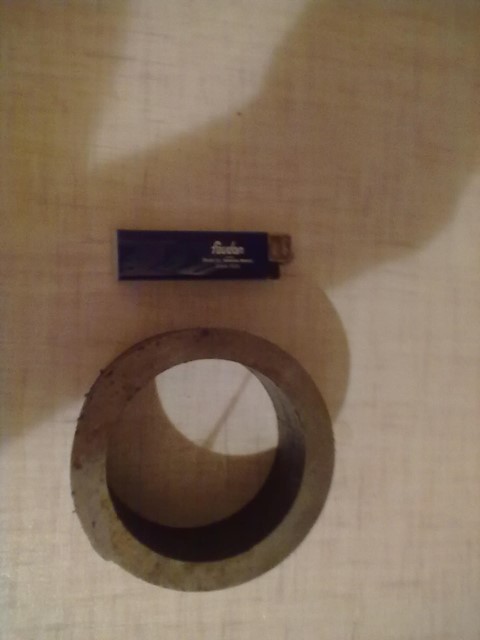

Fig. 4. Our second magnet
Conclusions
- The ions Na+ and Cl- which drift from salt to fresh water, could be separated by magnetic field.
- Ever a weak magnetic field of magnet from radio speaker could perform ion separation, which is necessary for creation electric field in 2 V/m.
References
- Княжев В. В. РЕСУРСЫ И СПОСОБЫ ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ЭНЕРГИИ ГРАДИЕНТОВ СОЛЕНОСТИ // Вестник ДВО РАН . 2010. №3. URL: http://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/resursy-i-sposoby-preobrazovaniya-energii-gradientov-solenosti (дата обращения: 18.11.2015).
- Михайлик, Б. Енерго- та ресурсозберігаючі технології. Осмотичні електростанції / Борис Михайлик // Наукові здобутки молоді – вирішенню проблем харчування людства у ХХІ столітті : програма і матеріали 80 міжнародної наукової конференції молодих учених, аспірантів і студентів, 10–11 квітня 2014 р. – К.: НУХТ, 2014. – Ч. 2. – С. 314-315.
- Вассель С.С., Вассель Н.П. Концепция концентрационного гальванического элемента, работающего на соленой и пресной воде // Современные научные исследования и инновации. 2014. № 5 [Электронный ресурс]. URL: http://web.snauka.ru/issues/2014/05/34761 (дата обращения: 22.10.2015).

 View this article in Russian
View this article in Russian