The reorganization and restructuring of power supply control and management, as wellas theconditions for their functioning, show their own complex features and problems. New algorithms, devices and methods are needed to ensure reliable electronicлектроsupply to consumers, involve modern information and diagnostic elements and devices and systems in the process of monitoring and managing operating modes. It is necessary to develop and apply new energy-efficient equipment and new technologies that reduce technical and economic indicators in the production and transmission of electricity, reduce the level of losses during transportation, optimize the size and location of reserve capacities of electricity sources [1-3].
As the analysis showed, in the last decade, the world has been developing Smart Grid technology (intelligent network). The existing “Smart grid” is a very large-scale direction in the modern energy industry. “Smart Grid” is the process of implementing ” smart solutions» generation, transmission and distribution of electric energy, saturation of the electric grid with modern diagnostic tools, electronic monitoring and control systems, algorithms, technical devices that have appeared today in science and technology, i.e. wide application of information technology capabilities [4-7],
Internet, digital technology (IoT) with power electrical engineering. And this reduces losses in the transmission of electrical energy from the generator to the consumer, increases the reliability of power supply, makes it possible to optimally redistribute energy flows and thereby reduce peak loads, makes it possible for the consumer to work in a unified powersupply system. Traditionally, the consumer received electrical energy from a single source, but now it is in a centralizedenvironment : можетit can choose the source among generating мощunits and sources [7-10].
The main feature in the “Smart Grid” is related to so-called renewable energy sources. To connect renewable energy sources to a large electricity supply system and make them as manageable as other sources, we need these “smart grids”Smart Grid. At the scale of power supply devices and systems, we need backbone or distribution networks that can monitor the state and mode of operation of consumers, sources, electrical lines and substations and automatically implement solutions that allow uninterrupted power supply and maximum economic efficiency. The “smart grid” itself must form a controlling influence with the achievement of an optimal level of electricity losses when the flow of electricity along transmission lines increases due to an increase in consumption by any consumer. In General, we are talking about creating a so-called intelligent EUSTC with an active adaptive network (IEUSTC), which means a power supply system in which all actors (generation, network, consumers) take an active part in the transmission and distribution of electricity. In this case, the electrical network turns into an active element, the parameters and characteristics of which change in real time depending on the modes of operation of consumers. To implement the new function, electric networks are equipped with modern high-speed electronic devices, systems that provide on-line information about the modes of operation of the network and the state of electrical equipment. Telecommunications devices and accumulators of electrical energy available in electric power supply networks ensure the process of distribution and consumption of electricity. Power supply systems are equipped with modern automation systems using powerful computer toolsforcontrolling and evaluating the state of operating modes [11-12].
Modern equipment is a complex energy of a new generation based on multi-agent principle, the organization and management of its functioning and development to ensure effective use of all resources (natural, socio-productive and human) for reliable, high-quality and effective elektrosnabzheniya of consumers due to the flexible interaction of all its subjects (all types of generation, power grids and consumers) on the basis of modern technological means and a single hierarchical intelligent control system [12-14].
In accordance with the modern requirements of power supply of electrical equipment and consumers, an algorithm for adaptive power management has been developed based on a simulation model (Fig. 1).
The algorithm for adaptive control of electricity supply while ensuring continuous energy transfer is based on the energy balance equation [5]:
where PCES(t), PSES(t), PWPP(t), PDG(t), PAB(t) - the values of power produced by sources of centralized electricity supply – (CES), solar power – (SES), wind power – (WES), diesel generators – (DG), batteries – (AB); Pn(t) - value of the power of the electrical load.
This algorithm controls the power supply sources and consumers by a microcontroller control unit based on the signals transmitted to the monitoring server about the amount of energy generated by the sources and consumed by the load, as well as the state of charge of batteries and the duration of use of sources Fig.1). [13]:
Monitoring data is collected and processed according to the scheme shown in Fig. 2. With this monitoring data accumulated in the server database monitoring and, if necessary, provided to the service personnel via an Ethernet Protocol in a web page on the Internet or the GSM module as SMS messages in the required formats.
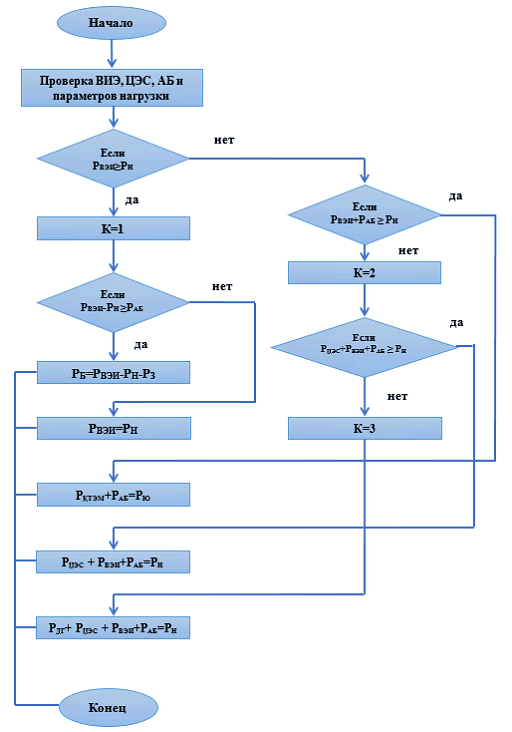
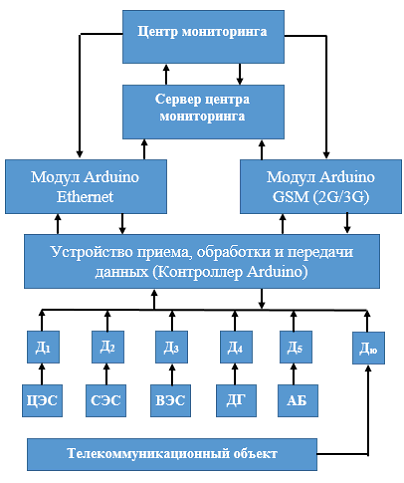
Fig. 2. Block diagram of remote monitoring of the power supply management process
RESULTS
As the analysis of electrical power networks and consumers, managed cosine of the capacitor unit are the main elements of the construction technology of “Smart grid” depending on the current electric networks, the power source of reactive power is proportional to the square of the voltage, frequency and capacity [2,4]:
![]() (1)
(1)
where:![]() - reactive power of the condenser unit;
- reactive power of the condenser unit;
![]() - electrical network voltage;
- electrical network voltage;
![]() is the angular frequency;
is the angular frequency;
C is the capacitance of the condenser unit.
The use of embedded microcomputers in the microprocessor source control unit of the Smart power engineering technology, depending on the load current, makes it possible to reduce damage from damage to electrical and power equipment and improve the quality of electricity generated [4-8].
For example, we will determine additional losses of active power ΔP in power supply system cable lines (CL1 +CL) 400 m long with a cross sectionof 50 mm2 [14]:
Let’s say that the power supply system had loads:
![]() ,
,
load factor
![]() ,
,
maximum power loss time: t =5000 h.
After applying smart technology, the object’s load will have the following values: ![]() .
.
The line current is defined as follows:
![]() (2)
(2)
![]() (3)
(3)
Additional power losses in the high-voltage cable (CL8):
![]() (4)
(4)
Additional ![]() TC power losses depend on its load
TC power losses depend on its load ![]() losses:
losses:
![]() (5)
(5)
Total power losses:
![]() (6)
(6)
Energy savings for the year will amount to:
![]() (7)
(7)
The increase in the capacity of the TC line can be accounted for by the corresponding shares of their cost.
For a vehicle power transformer:
![]() (8)
(8)
For cables with a long current tolerance![]() :
:
![]() (9)
(9)
Payback period of the proposed technology:
![]() (10)
(10)
The performance indicator for this event is defined as follows:
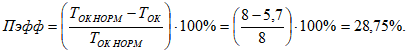 (11)
(11)
The developed algorithm and methodology for calculating technical and economic indicators gives a pessimistic payback period for the use of smart technology in power supply systems. The obtained value of the payback period, due to improving the quality of electricity – providing rated voltage in power consumption units (i.e., increasing the service life of electrical equipment, reducing power losses in electrical networks, etc.), actually turns out to be less than its normative value (TOK norms = 8 years).
A. Parameters of the regulated reactive power compensation technology (number and power of control stages) – are determined by the daily schedule of electricity consumption by electric receivers.
B. Technology of controlling reactive power sources and voltage regulation is effective when switching on for a large inductive resistance of step-down transformers of power supply systems.
C. To change the voltage by one percent of the rated value, it is necessary for the transformer ![]() to change the reactive power to
to change the reactive power to ![]() , for the transformer
, for the transformer![]() , for the cable line
, for the cable line ![]() length
length![]() , for the cable line
, for the cable line ![]() length
length ![]() .
.
As shown by the research, the proposed method of applying smart technology for controlling reactive power sources and microprocessors allows to reduce the payback period of the implemented technology and control elements of electricity consumption by 28.7% and increase the efficiency of energy-saving measures implemented in power supply systems
D. the monitoring System makes it possible to assess their operational characteristics, determine the repair needs, identify the causes of failure and promptly eliminate them.
The use of monitoring systems allows you to increase reliability through high-quality maintenance by reducing the time of prevention, repair, recovery and downtime.
The developed algorithm and sensors for controlling electricity sources and consumers, as well as the use of monitoring devices, allow for continuous power supply, adaptability to the power sources of the control unit, and a user-friendly control interface allows for high accuracy and efficiency of management.
References
- I. Kh.Siddikov., Kh. A.Sattarov., H. E. Hamatov., G. S. Rakhmonov. Electromagnetic Converter of three-phase current into voltage for electrical networks of power supply systems of telecommunications devices / / “TATU khabarlari” ilmiy-texnika va axborot-tahliliy jurnali. №3(43), 2017, Pp. 114-119. (05.00.00; №10).
- I. Kh.Siddikov., Kh. A.Sattarov., H. E. Hamatov., O. R. Dehkonov. Improving the efficiency of electric networks of telecommunications facilities based on the use of reactive power sources / / “Muhammad al-Xorazmiy avlodlari” ilmiy-amaliy va axborot-tahliliy jurnal. №2(4), 2018, Pp. 80-83. (05.00.00; №10).
- Kh.E. Khujamatov., Kh.A. Sattarov., Kh.A. Najmidinov., M.A. Anarbayev. Modeling and research of the processes of control of hybrid power supply systems / / “Information technologies and modeling of processes in fundamental and applied research” Materials of the I International youth school-conference, Astrakhan December 15-17, 2016, Pp. 151-157.
- I.Kh. Siddikov., Kh.A. Sattarov., Kh.E. Khujamatov., K.S. Sherjanova. Modeling of the elements and devices of energy control systems // Materials of the XXXII International scientific and practical Internet conference “Trends and prospects for the development of science and education in the context of globalization” 31 January 2018. Pereyaslav-Khmelnitsky, Pp. 466-468.
- Siddikov I. Kh., Khuzhamatov Kh. E. Software for managing hybrid power sources based on consumer accounting / / no. DGU 05353 Agency for intellectual propertyOf the Republic of Uzbekistan. – Tashkent, 25.06.2018.
- Allaev K. R. Energetika Mira I Uzbekistana [energy Of the world and Uzbekistan]. Tashkent: Moliya publ., 2006, 388 p. (in Russian).
- Махсудов М. Т., Бойхонов З. У. Исследование электромагнитных преобразователей тока в напряжение // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2018. Т. 4. №3. С. 150-154. Режим доступа: http://www.bulletennauki.com/mahsudov (дата обращения 15.03.2018)
- Borodenko V. A. resource Saving as the main principle of creating automation devices of power systems // Vestnik NIA RK, Moscow, 2006, no. 2.12 p.
- PatentRUz. №04185. Three-phase current-to-voltage unbalance Converter/Amirov S. F., Azimov R. K., Siddikov I. Kh., Khakimov M. H.,Hushbokov B. H.,Sattarov Kh. a. Rasmiy akhborotnoma. -2010. №6.
- Regulation on the procedure for organizing work on reactive power compensation // Teshabayev B. M., Yusupaliev M. M, Saliev A. G., The Siddiqui I. H., Umarov F. U. / Approved N 1864 of 10.10.2008. justice Ministry. Of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Tashkent, GIUsawanhouse. 2008. 24 p. (in Russian).
- Yusupbekov N. R., Key Z. Kh., Malikov A.V. Bases of automation of technological processes: a tutorial. In 2-2 hours. – Tashkent: TSTU, 2007. ЧH1-2 – – 152, 115 s .
- Krontiris E., Hanitch R., Paralika M., Rampias I., Stathais E., Nabe A., KadirovT.M., Siddikov I.Kh., Energy Management raining in Uzbekistan // ThefinalreportoftheProjectECTJEP-10328 – 97. TU – Berlin (Germany), TEI -Athens (Athens, Greece),TashGTU (Tashkent, Uzbekistan), 1997-2001. – 234 р.
- Siddikov I. Kh., Boikhonov Z. U., Karimjonov D. D. Elements And Devices For Monitoring And Controlof Energy Efficiency. The American Journal of Engineering and Technology (ISSN – 2689-0984) Published: September 29, 2020 | Pages: 136-148.
- Siddikov I. Kh., Boikhonov Z. U, Makhsudov M. T., Uzaqov. R. Features productions reactive power onsystems electrical supply with renewable sources energies. Academicia: an international multidisciplinary research journal vol. 10, issue 6, June 2020 Pages: 292-296
- Эгамов, Д. А. Эффективность применения «переносного АВР-0,4 кВ» для обеспечения бесперебойного электроснабжения потребителей / Д. А. Эгамов, Р. Узаков, З. У. Боихонов // Исследования и разработки в области машиностроения, энергетики и управления : материалы XIX Междунар. науч.-техн. конф. студентов, аспирантов и молодых ученых, Гомель, 25–26 апр. 2019 г. / М-во образования Респ. Беларусь, Гомел. гос. техн. ун-т им. П. О. Сухого ; под общ. ред. А. А. Бойко. – Гомель : ГГТУ им. П. О. Сухого, 2019. – С. 250-253.
- Эгамов Д. А., Узаков Р., Бойхонов З. У Способы обеспечения бесперебойного электроснабжения потребителей, имеющих одну систему шин 6-10 кВ и два независимых источника питания 6-10 кВ // Бюллетень науки и практики. 2018. Т. 4. №3. С. 155-159. Режим доступа: http://www.bulletennauki.com/egamov-uzakov (дата обращения 15.03.2018).
